Deploy request-baskets on IBM Cloud Code Engine using Terraform
Run the request-baskets application on IBM Cloud Code Engine with persistent storage provided by an IBM Cloud PostgreSQL instance.
Overview
In this post, we will deploy the request-baskets application on IBM Cloud Code Engine using Terraform. The request-baskets application is a simple HTTP requests collector that can be used to test webhooks, notifications, REST clients and more. The application stores the requests in a PostgreSQL database and provides a web interface to view the requests.
Prerequisites
Getting started
Clone the repository
First, clone the request-baskets terraform repository:
git clone https://github.com/cloud-design-dev/ibmcloud-tf-ce-request-baskets.git
cd ibmcloud-tf-ce-request-basketsSet Terraform environment variables
Copy the terraform.tfvars.example file to terraform.tfvars, open it in a text editor and set the following variables:
- ibmcloud_api_key: Your IBM Cloud API key.
- ibmcloud_region - The IBM Cloud region where you want to deploy the resources. Default is
us-south. - existing_resource_group - The name of the resource group where you want to deploy the resources.
- existing_postgres_instance - The name of the existing PostgreSQL instance where you want to store the requests.
- project_owner - Owner to associate with the project. Will be used as a tag for the resources.
Initialize Terraform
Run the init command to initialize Terraform in the directory and download the required providers and modules:
terraform initGenerate the Terraform plan
Run the following command to generate a Terraform plan and save it to the file default.tfplan:
terraform plan -out default.tfplanOur plan output should show the resources that will be created, updated, or deleted. On the initial run we should see that the following resources will be created:
- IBM Cloud Databases for PostgreSQL instance (optional, if you don’t have an existing PostgreSQL instance)
- Service credentials for the PostgreSQL instance
- IBM Cloud Code Engine project
- IBM Cloud Code Engine application
- IBM Cloud Code Engine ConfigMap and Secret for PostgreSQL connection details
- Request-baskets master token. This allows you to see all baskets created by other users.
Apply the Terraform plan
Run the following command to apply the Terraform plan:
terraform apply default.tfplanThe Code Engine project will take a few minutes to get created. Once the project is created, Terraform will deploy our application using the request-baskets container image and add our PostgreSQL connection details to the running instance as environment variables.
terraform apply "default.tfplan"
...
...
ibm_code_engine_app.request_baskets: Still creating... [10s elapsed]
ibm_code_engine_app.request_baskets: Still creating... [20s elapsed]
ibm_code_engine_app.request_baskets: Still creating... [30s elapsed]
ibm_code_engine_app.request_baskets: Still creating... [40s elapsed]
ibm_code_engine_app.request_baskets: Still creating... [50s elapsed]
ibm_code_engine_app.request_baskets: Still creating... [1m0s elapsed]
ibm_code_engine_app.request_baskets: Creation complete after 1m0s [id=xxxx-yyy-zzz/lqjv-rb-app]
Apply complete! Resources: 8 added, 0 changed, 0 destroyed.
Outputs:
app_url = "https://lqjv-rb-app.1glfavnwqwgu.us-east.codeengine.appdomain.cloud"
db_connection_details = <sensitive>
request_basket_master_token = "xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx"When the Terraform apply is complete, you will see the database connection details. the URL of the application, and the request-baskets master token in the Terraform output. Grab the URL and toss it in the browser to see the application in action.
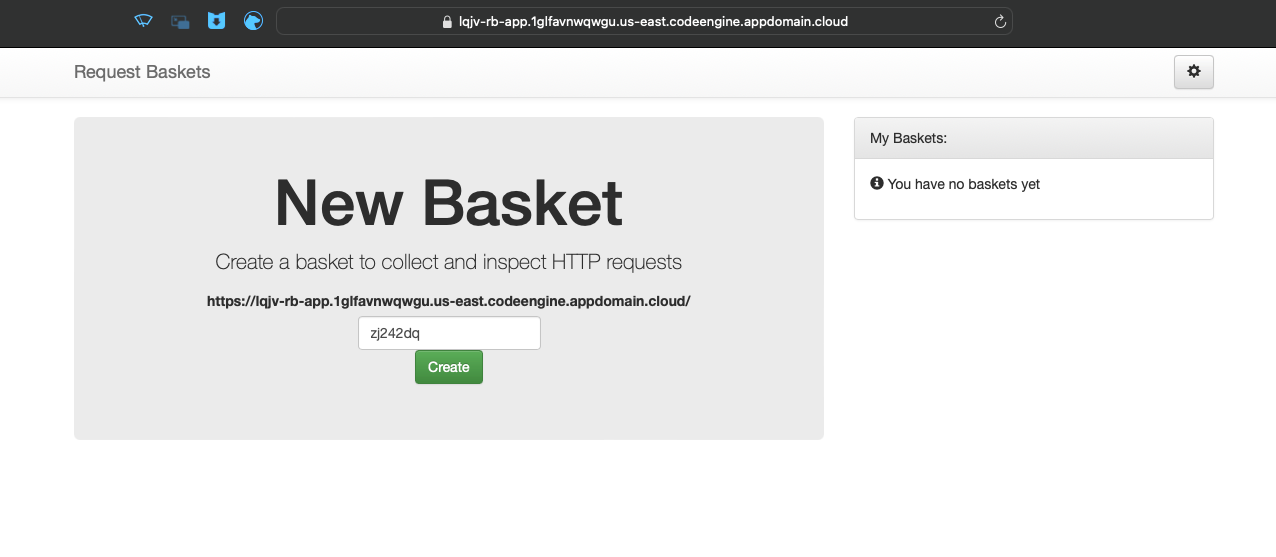
The UI will auto-generate a basket name for you, but you can also give it a custom name. Click Create to create a new basket and start sending requests to it. You will see a pop-up with the basket name and the basket token. You can use the basket token or master token to view the requests in the basket.
Note: The token is automatically saved in your session, so you can view the requests in the basket without entering the token again. If you close the tab or refresh the page, you will need to enter the token again to view the requests.
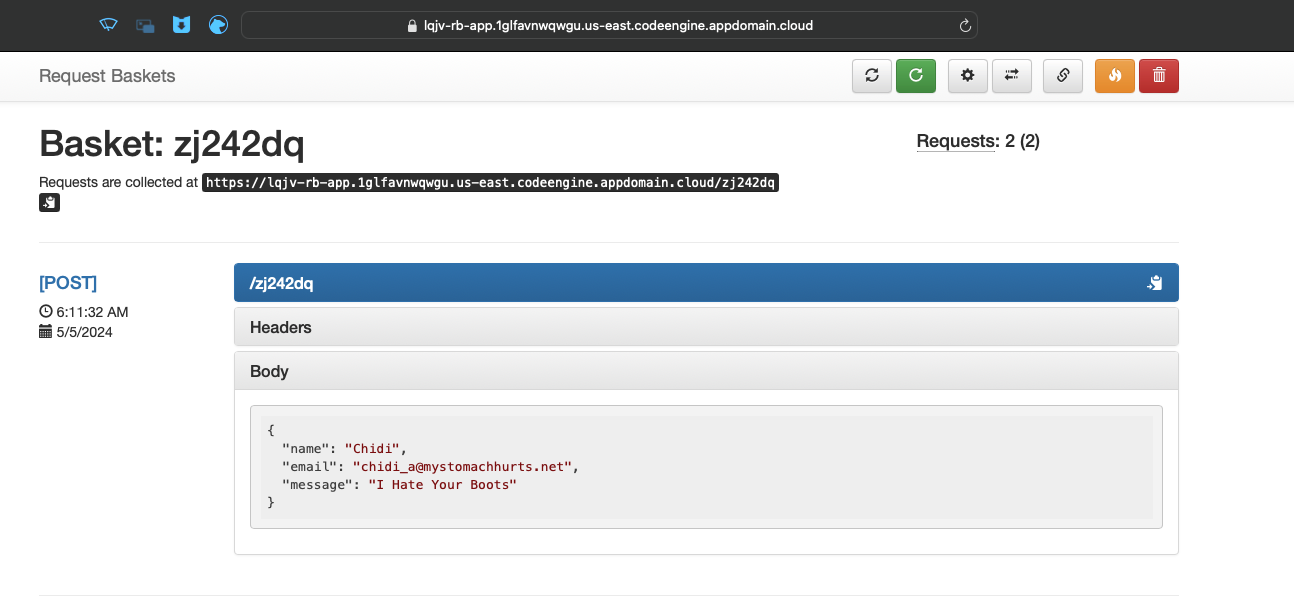
With the new basket created, let’s send it some data and see the results. You can use the curl command to send a request to the basket. Replace YOUR_CODE_ENGINE_URL with the URL of your application:
curl -X POST https://YOUR_CODE_ENGINE_URL/YOUR_BASKET_NAME -d '{"name": "Chidi", "email": "chidi_a@mystomachhurts.net", "message": "I Hate Your Boots"}' Our basket page should refresh and show the new request.
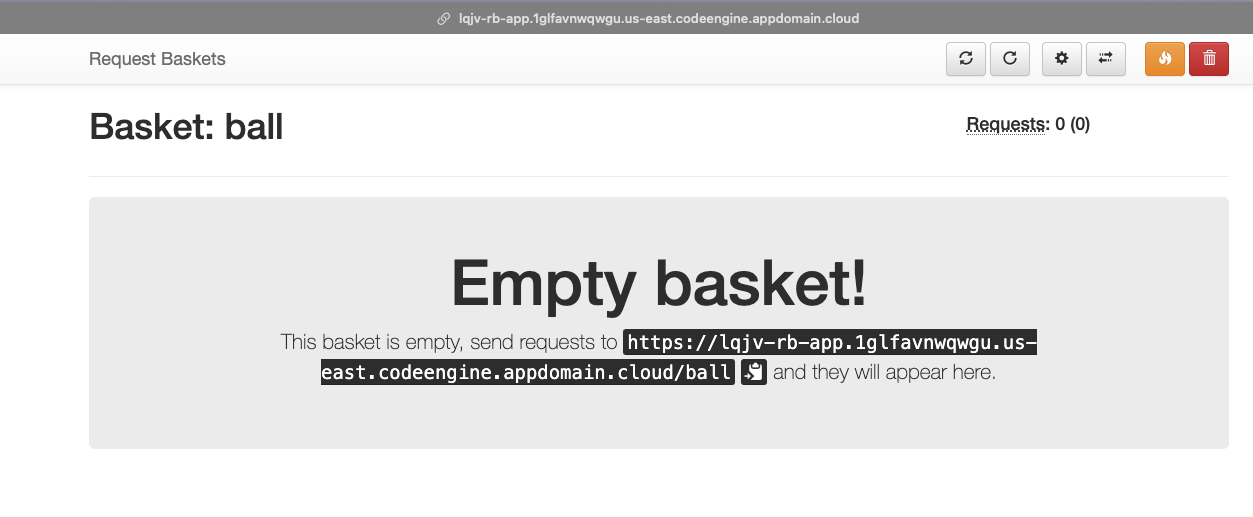
Inspect the basket ball
During the creation of our application, we also set a default basket with the name ball. You can use the master token to view the requests in the basket ball at https://YOUR_CODE_ENGINE_URL/web/ball.
Clean up
To clean up the resources created by Terraform, run the following command:
terraform plan -destroy -out destroy.tfplan
terraform apply destroy.tfplanWrap-up
In this post, we deployed the request-baskets application on IBM Cloud Code Engine using Terraform with persistent storage backed by an IBM Cloud PostgreSQL instance.